Muscular Endurance Is Fueled by Anaerobic Energy
4 a form of exercise that involves short intense bursts of energy. Log in for more information.

Fuel Sources For Exercise Nutrition Science And Everyday Application
Up to 24 cash back However it has larger fuel supplies a bigger fuel tank and doesnt burn all its fuel as quickly as the ATP-CP system so it doesnt fatigue as quickly as the ATP-PC system.
. Muscular endurance is fueled by anaerobic energy. To produce more energy your body uses its anaerobic system which relies on energy sources stored in your muscles. Asked 6192013 82234 AM.
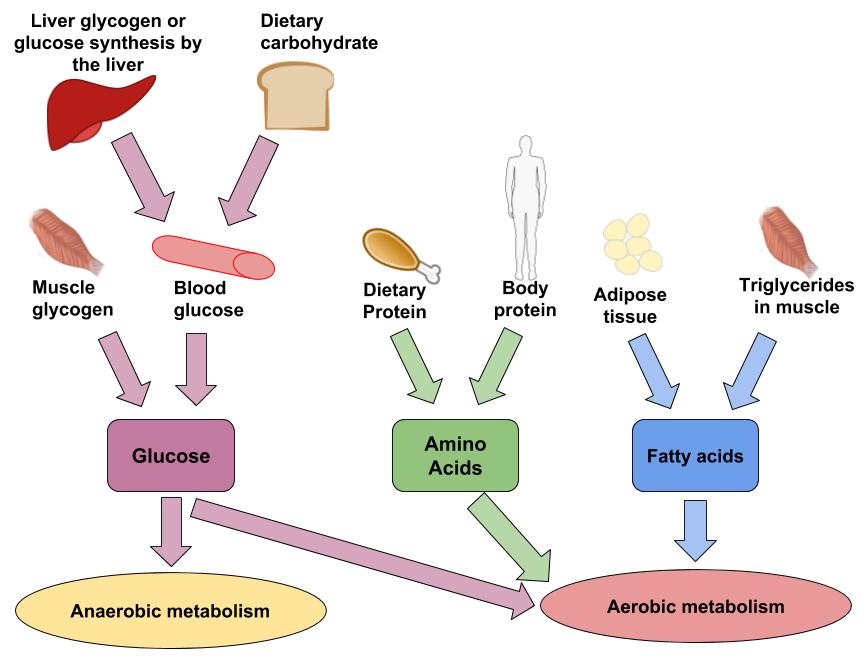
Fuel for the anaerobic lactic system comes from glucose stored in the muscles and liver. Anaerobic exercise can only be maintained for 1-2 minutes slightly longer through specific anaerobic training. Added 5272020 105323 AM.
Darmaidayxx and 1 more users found this answer helpful. 2 The immediate anaerobic energy system. Short-term anaerobic energy system.
This answer has been confirmed as correct and helpful. Anaerobic exercises are generally used to build muscle mass increase muscular strength speed and power for example sprinting running cycling swimming etc and bodybuilding. Log in for more information.
Correct answer to the question Muscular endurance is fueled by anaerobic energy. Updated 10102017 41929 AM. Muscular strength is the amount of force a muscle or group of muscles can exert.
When muscles contract they break down ATP in a reaction that provides energy. Muscular endurance is fueled by anaerobic energy. Slower-paced exercises like jogging or endurance cycling are examples of aerobic.
Muscular endurance is fueled by anaerobic energy. Log in for more information. Once muscle contraction starts the making of ATP must start quickly.
Is Muscular Endurance Fueled By Anaerobic Energy True. However muscle cells only store enough ATP to fuel a few seconds of maximal contraction. The anaerobic energy system is the energy system of choice for the 100m sprinter.
The correct answer to your question is for that reason B - False. This answer has been confirmed as correct and helpful. Muscular endurance is fueled by anaerobic energy.
Muscle glycogen is the primary fuel used during endurance exercise. Our bodies can create anaerobic energy in two ways through the. See answer 1 Best Answer.
Anaerobic capacity is the amount of work performed using primarily anaerobic energy system. When your muscles demand for energy surpasses your lungs and hearts abilities to deliver oxygen your muscles have to burn energy glycogen without O2 which is. Anaerobic - without oxygen as your muscles work faster and harder they require more energy and thus more oxygen.
Muscular endurance is fueled by anaerobic energy. Immediate anaerobic energy system and. Your lungs breathe deeper and your heart beats faster trying to keep up with the demand.
Anaerobic energy systems in skeletal muscle. Neither system provides sustainable energy for very long. The energy system that fueled the majority of his exercise was.
The most significant factor leading to exhaustion during intense endurance exercise lasting 15 to 25 hours is. There is a reason why running Which is considered an endurance activity is also at the same time considered to be an aerobic exercise while heavy weight-lifting is considered to be a anaerobic exercise. ATP is a high-energy nucleotide which acts as an instant source of energy within the cell.
It is the ability to perform brief maximal muscular activity and ability to supply energy without the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic means without oxygen. ANAEROBIC ENDURANCE CAPACITY.
Catabolism and anabolism are the two phases of metabolism. Muscular endurance is NOT fueled by anaerobic energy. Log in for more information.
Muscular strength is the amount of force a muscle or group of muscles can exert. Anaerobic power is strongly related to explosive movements. Examples of muscular endurance involving the anaerobic lactic acid system include.
Exercise Energy Systems A Primer
Fuels For Exercise Aerobic Or Anaerobic Exercise Intensity And Duration

Fuel Sources For Exercise Nutrition Science And Everyday Application
Comments
Post a Comment